Activation Energy | Represents the energy that a molecule in the initial state of the process must acquire before it can take part in a reaction. |
| Calibration Curve | Same as the “Maturity Curve” |
| Compressive strength | The strength recorded from compression tests |
| Concrete mix | Any mixture containing cementitious material and water |
| Curing time | The time from concrete placement until the current time |
| Datum temperature | Datum temperature is the temperature at which concrete stops its strength development |
| Early-age strength | The strength within the first few hours or days after casting concrete (normally up to 14 days) |
| Equivalent age | The maturity index computed from the measured temperature history of concrete in the Arrhenius function |
| Final strength | The required strength after 28 days |
| Hydration | The chemical reaction that leads to changes that take place when cement reacts with water |
| In-place strength | The estimated strength of the field concrete |
| Maturity | Concrete maturity indicates how far a concrete mixture is in its curing process and it represents the relationship between time, temperature and strength gain |
| Maturity curve | A curve presenting the strength-maturity relationship to be used for estimating the strength of the concrete mixture cured under other temperature conditions |
| Maturity function | A maturity function is a mathematical expression to account for the combined effects of time and temperature on the strength development of a cementitious mixture. The key feature of a maturity function is the representation of how temperature affects the rate of strength development |
| Maturity index | An indicator of maturity that is calculated from the temperature history of the cementitious mixture by using a maturity function |
| Maturity instrument | A device that records the concrete temperature as a function of time |
| Maturity method | A technique for estimating concrete strength based on the assumption that samples of a given concrete mixture attain equal strengths if they attain equal values of the maturity index |
| Maturity sensor | Sensor that is able to measure time-based temperature |
| Samples | Concrete cylinders or cubes normally used for testing purposes |
| Set time | The time at which a concrete surface can bear the weight of an individual with minimal deformation |
| Specimen | See: “Samples” |
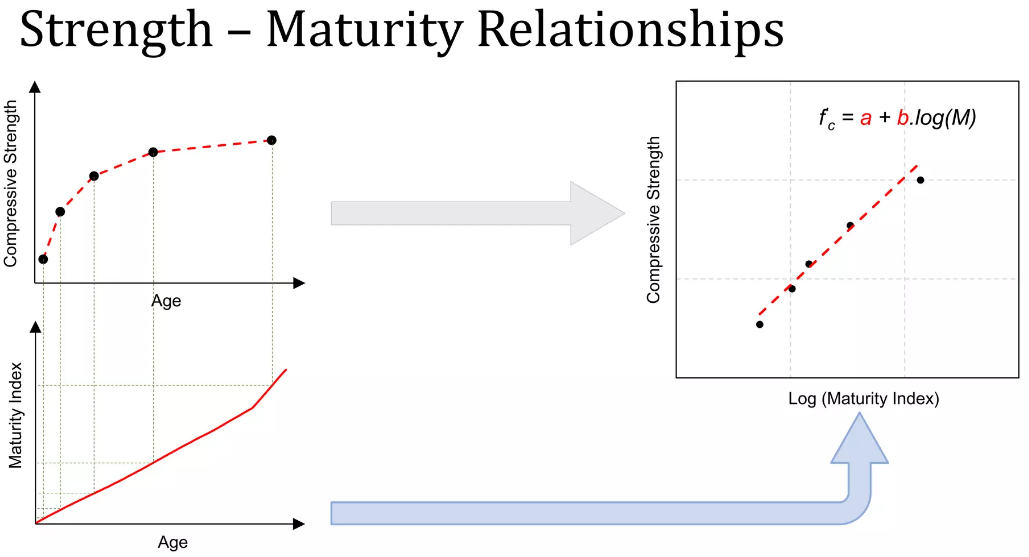
| Strenght-Maturity relationship | The relationship between the compressive strength and maturity index that is obtained by testing samples and recording their temperature history |
| Target strength | The required strength before proceeding to the next project step |
| Temperature-time factor | The maturity index computed from the measured temperature history of concrete in the Nurse-Saul function |
| Test age | The time from concrete placement until the compression test |